- What is SQLAlchemy?
- SQLAlchemy Core Python
- SQLAlchemy Core Insert
- SQLAlchemy Core Select
- SQLAlchemy Core Update
- SQLAlchemy Core Delete
I will jump right into a simple example using Jupyter Notebook with Anaconda Navigator. Here we have a Python project that is connecting to a SQLite database using the ORM SQLAlchemy.
import sqlalchemy as sa sqlalchemy.__version__
'1.4.39'
I am using version 1.4.39. Yours may be different. I ran this code in November 2024. The name of our new SQLite database is emp.db, as you can see in the code below.
engine = sa.create_engine('sqlite:///emp.db')
connection = engine.connect()
meta_data = sa.MetaData()
employees = sa.Table(
'Employees', meta_data,
sa.Column('id', sa.Integer(), primary_key=True),
sa.Column('name', sa.String()),
sa.Column('position', sa.String())
)
meta_data.create_all(engine)
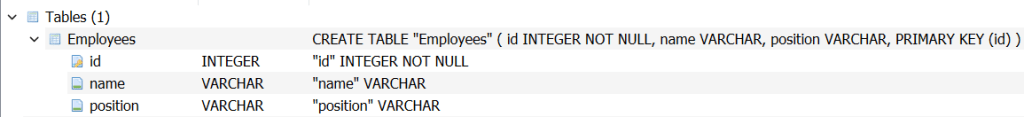
The database is created in your current directory. What is the current directory? Because I am using Anaconda Navigator in Windows here, the current directory is where the project is stored, which is C:\users\username where username is the Windows user. This below is what it looks like in DB Browser.
Here is the syntax if you want to specify a folder location in Windows. By the way, single quotes also work.
engine = sa.create_engine(r"sqlite:///D:\Test\emp2.db")
print(employees.insert())
INSERT INTO "Employees" (id, name, position) VALUES (:id, :name, :position)