Here is a simple VBA example that creates a small table of data with a bold header, wherever the user places the cursor. It uses ActiveCell, Font, Bold FormulaR1C1 and Offset. The two parameters of offset are Row, Column and these are integers that can be positive or negative. An offset of 0, 1 means to stay on the same row and move over one column to the right. In this example, the user has placed the cursor in cell B2 before running the code.
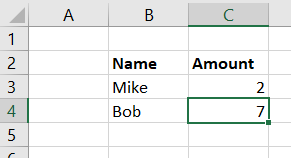
Sub MySmallTable() 'Name Amount 'Mike 2 'Bob 7 ActiveCell.Font.Bold = True ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "Name" ActiveCell.Offset(0, 1).Select ActiveCell.Font.Bold = True ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "Amount" ActiveCell.Offset(1, -1).Select ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "Mike" ActiveCell.Offset(0, 1).Select ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = 2 ActiveCell.Offset(1, -1).Select ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "Bob" ActiveCell.Offset(0, 1).Select ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = 7 End Sub
If we wanted to force the creation of this table to start in cell A1 then we could simply, at the top of our program, select that cell with either of the following two lines of code. You can also use the Row, Column method as you can see in line 4.
Range("A1").Select
ActiveSheet.Range("A1").Select
'To select cell B5 on the active worksheet, you can use:
ActiveSheet.Cells(5, 2).Select
Suppose you want to also enter in a formula to SUM the totals of the Amount column. You would need to add the following two lines of code to the bottom of our MySmallTable routine.
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "=SUM(R[-2]C:R[-1]C)"